
SOC 2 Compliance stands for System and Organization Controls 2, a framework developed by the American Institute of CPAs (AICPA). The purpose of this framework of SOC2 report is to provide the health status of a company’s data handling. This framework is not industry-specific, but covers any company whose customer data resides in the cloud.
Now, the question is why are we talking about this. Data handling has a prime concern in the wake of data breach incidents hitting headlines every week. In the IT environment, companies need to work with many vendors, but would you like to work with a vendor whose customer data handling practices are questionable. The SOC2 compliance report has become the standard proof that you take data security seriously
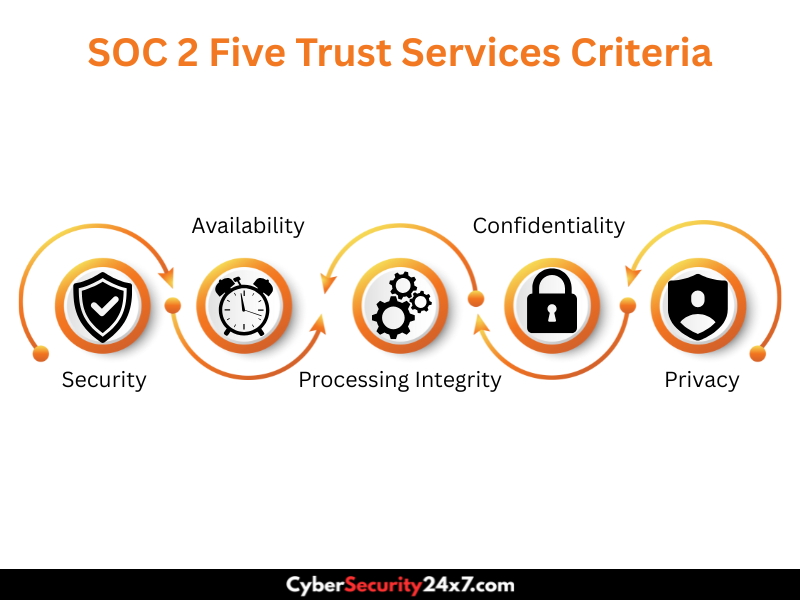
The framework has five pillars as a foundation: Security, Availability, Processing Integrity, Confidentiality, and Privacy. To follow SOC 2 Compliance, you don’t need to implement all five components. Most companies start with Security as this is the most important pillar since every other thing sits at the top of the security. .
In this blog, we will walk through SOC2 compliance, types of SOC2 compliances and differences between SOC1 and SOC 2 compliances.
Let’s start our journey!
SOC 2 Compliance defines how organizations should manage and safeguard customer data according to five Trust Services Criteria (TSC), which includes the following
For security teams, SOC 2 framework is not merely about security audit but it builds a robust and repeatable process for safeguarding sensitive data through access controls, incident response plans, change management procedures, continuous monitoring, and robust documentation.
A mature SOC 2 program helps security teams:
It also forces a culture of accountability—ensuring that security is a shared responsibility across IT, engineering, and leadership, not just a checkbox exercise for compliance.
SOC 2 compliance, in short, creates both a security baseline and a trust signal for customers, investors, and partners—positioning security teams as enablers of growth rather than cost centers.These reports come in two types:
Type 1 SOC 2 compliance report checks security controls are properly designed at a specific moment in time. A security auditor reviews your policies and systems on a defined date to validate the necessary safeguards are in place.
For example, if a company implements access controls on January 1, a Type 1 report confirms that these controls existed and were appropriately designed on that day.
SOC 2 Type 1 is most useful when:
Limitations:
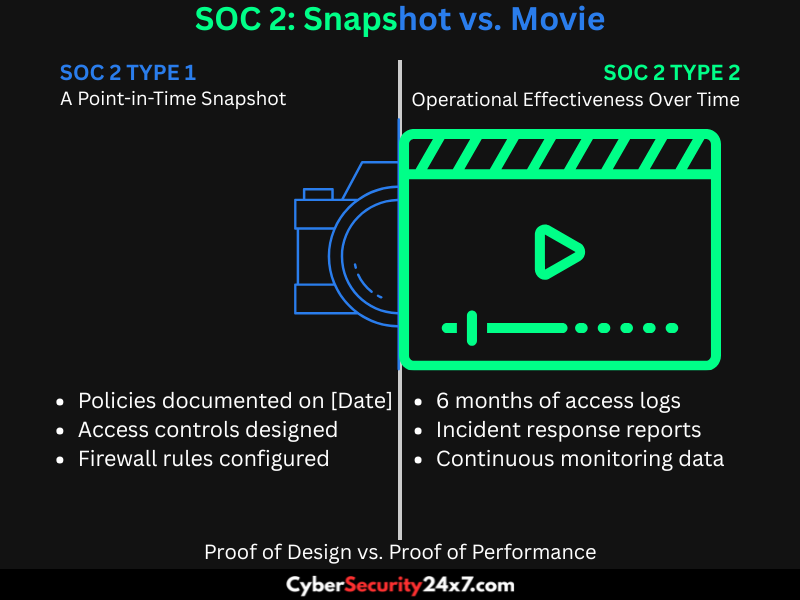
SOC 2 Type 2 reports adopt a more comprehensive and strict approach towards controls operated over a period. It is applicable in the range of six to twelve months. The audit reviews evidence such as logs, incident responses, and employee training records to verify that controls are not only in place but also effective in practice.
The type 2 level provides a greater degree of assurance about data handling practices. It is often required by enterprise-grade companies.
For instance, a startup might initially pursue a Type 1 report to demonstrate that security systems are appropriately structured. But as the company matures and attracts more significant clients, a Type 2 report becomes necessary to prove consistent and reliable control implementation over time.
SOC 2 type 2 report is most useful when:
Advantages:
Challenges:
Purpose
Type 1: Evaluates whether controls are properly designed and implemented at a single moment in time. This is like taking a snapshot to see if everything is set up correctly that day.
Type 2: Examines both the control design and whether they consistently work as intended over several months, offering deeper insight into actual operational performance rather than a one-time setup.
Audit Focus
Type 1: Checks that documented controls truly exist and are suitably designed on a specific date, without testing their long-term reliability or day-to-day operational effectiveness.
Type 2: Confirms that controls are not only designed well but also operate effectively and reliably in real-world business scenarios across the audit period, ensuring ongoing trust in operations.
Audit Period
Type 1: Captures a single-day assessment, providing a quick compliance snapshot that reflects how controls appeared and functioned on that chosen date only.
Type 2: Spans several months, enabling auditors to observe how controls perform under various conditions, workloads, and real-life events, offering a much more comprehensive risk picture.
Depth of Assurance
Type 1: Delivers limited assurance—proves that the right processes and tools are in place, but without verifying how consistently they perform over time.
Type 2: Provides stronger assurance by confirming that controls maintain their effectiveness and reliability continuously, reducing the chance of hidden vulnerabilities going undetected.
Time & Cost
Type 1: Quicker and more affordable to complete, often within weeks, making it practical for startups or companies with urgent contractual needs.
Type 2: Requires more time, resources, and auditor involvement due to extended monitoring and evidence gathering, resulting in higher costs but deeper trust.
Project Management
Use Case
Type 1: Ideal for companies early in their security journey or those needing immediate proof of controls to win contracts or meet initial compliance requests.
Type 2: Best for established organizations working with large, security-conscious clients or industries where long-term operational consistency is critical for vendor approval.
Report Detail
Type 1: Contains management’s assertion, a system description, and detailed control listings, but no real-world operational testing results.
Type 2: Includes all Type 1 information plus results of control testing, documented findings, and any exceptions encountered during the monitored period.
Trust Services Criteria (TSC)
Type 1: Must include Security, with optional focus on Availability, Processing Integrity, Confidentiality, or Privacy depending on scope, but without proof of long-term control effectiveness.
Type 2: Uses the same criteria but requires demonstrating control effectiveness for the entire audit period, offering stronger evidence to clients and regulators.
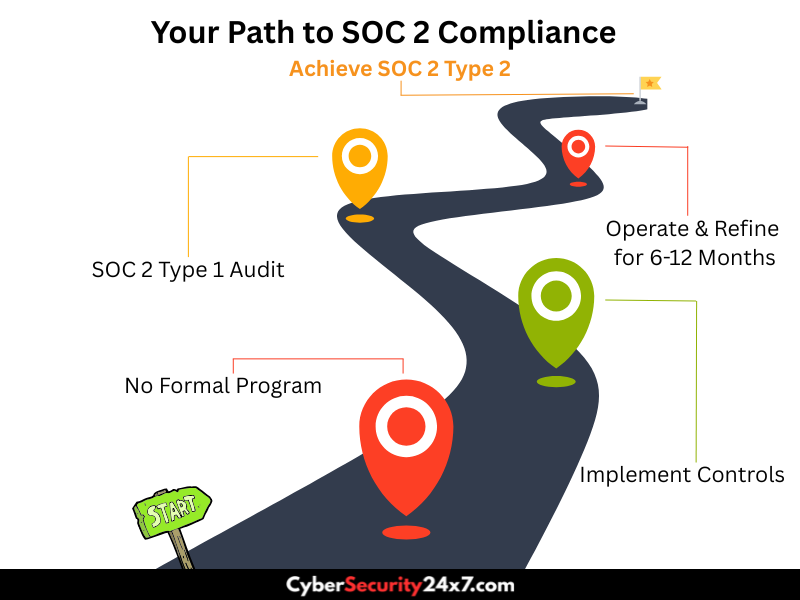
In the end, pick the SOC 2 report that fits your security maturity, business ambitions, and market pressures. The right choice builds trust today and sets you up for long-term growth.
Ignoring data handling processes can pose SOC 2 compliance risks for your company. Our experts can help manage the compliances better. Contact us now to learn more.
Also Read our detailed blog on GDPR : General Data Protection Regulation.